Welcome to Neilpang's Blog!
记录生活,分享知识,传播乐趣-
解决:Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1 cannot be loaded because the execution of scripts is disabled on this system. Please see “get-help about_signing” for more details.
在执行powershell启动脚本的时候. 会报这个错
Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1 cannot be loaded because the execution of scripts is disabled on this system. Please see “get-help about_signing” for more details.
原因是因为windows默认启用了安全策略, 禁止启动脚本.
查看策略:
PS C:\Windows\System32> Get-ExecutionPolicy
Restricted
PS C:\Windows\System32>需要关闭它:
PS C:\Windows\System32> Set-Executionpolicy -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
这样就好了.
参考: http://www.christiano.ch/wordpress/2009/07/26/solution-microsoft-powershell_profile-ps1-cannot-be-loaded-because-the-execution-of-scripts-is-disabled-on-this-system-please-see-get-help-about_signing-for-more-details/
-
转载:Ubuntu查看系统的信息命令大全
系统信息
# uname -a # 查看内核/操作系统/CPU信息
# cat /etc/issue # 查看操作系统版本
#cat /proc/version #包含GCC的版本信息
# cat /proc/cpuinf # 查看CPU信息
# hostname # 查看计算机名
# lspci -tv # 列出所有PCI设备
# lsusb -tv # 列出所有USB设备
# lsmod # 列出加载的内核模块
# env # 查看环境变量资源信息
# free -m # 查看内存使用量和交换区使用量
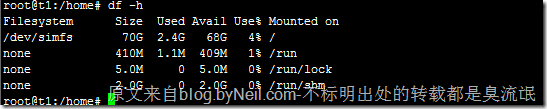
# df -h # 查看各分区使用情况
# du -sh <目录名> # 查看指定目录的大小
# grep MemTotal /proc/meminfo # 查看内存总量
# grep MemFree /proc/meminfo # 查看空闲内存量
# uptime # 查看系统运行时间、用户数、负载
# cat /proc/loadavg # 查看系统负载磁盘信息
# mount | column -t # 查看挂接的分区状态
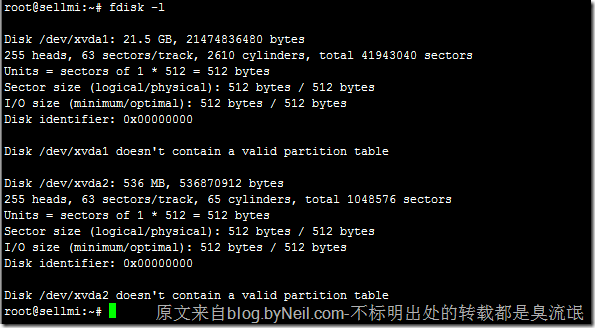
# fdisk -l # 查看所有分区
# swapon -s # 查看所有交换分区
# hdparm -i /dev/hda # 查看磁盘参数(仅适用于IDE设备)
# dmesg | grep IDE # 查看启动时IDE设备检测状况网络信息
# ifconfig # 查看所有网络接口的属性
# iptables -L # 查看防火墙设置
# route -n # 查看路由表
# netstat -lntp # 查看所有监听端口
# netstat -antp # 查看所有已经建立的连接
# netstat -s # 查看网络统计信息进程信息
# ps -ef # 查看所有进程
# top # 实时显示进程状态用户信息
# w # 查看活动用户
# id <用户名> # 查看指定用户信息
# last # 查看用户登录日志
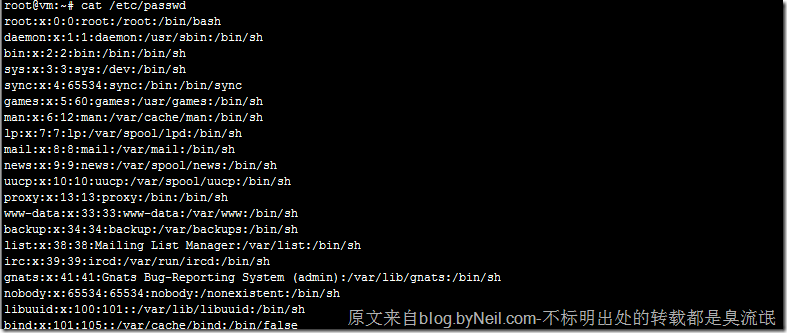
# cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd # 查看系统所有用户
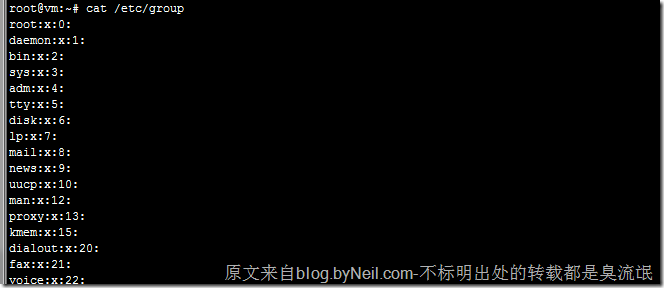
# cut -d: -f1 /etc/group # 查看系统所有组
# crontab -l # 查看当前用户的计划任务
-
useradd,groupadd 添加用户和用户组
id命令可以查看当前用户的详细信息:
root@vm:~# id uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)- 在
/etc/group文件中记录着所有的用户组:
root@vm:~# cat /etc/group- 在
/etc/passwd文件中记录了所有的用户的信息
root@vm:~# cat /etc/passwd添加用户组:
root@vm:~# groupadd backupuser禁止用户组访问网络:
iptables -A OUTPUT -m owner --gid-owner backupuser -p all -j DROP保存 iptables设置:
iptables-save > ip.conf恢复iptables设置:
iptables-restore < ip.conf需要写入开机脚本,确保每次重启生效。
/etc/rc.local添加用户,指定组, –m 自动生成home文件夹
useradd user1 -g backupuser -m未完, 待续…….
-
fstab,mtab,mount,fdisk 查看系统磁盘详情
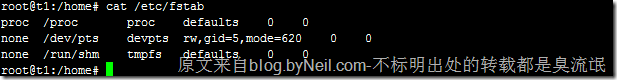
fstab 文件想必大家都很熟悉,记录了计算机上硬盘分区的相关信息,启动 Linux 的时候,检查分区的 fsck 命令,和挂载分区的 mount 命令,都需要 fstab 中的信息,来正确的检查和挂载硬盘。
root@t1:/home# cat /etc/fstab
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
none /dev/pts devpts rw,gid=5,mode=620 0 0
none /run/shm tmpfs defaults 0 0除了 fstab 文件之外,还有一个 mtab 文件,和 fstab 文件一样在 /etc 文件下,位于 /etc/mtab。
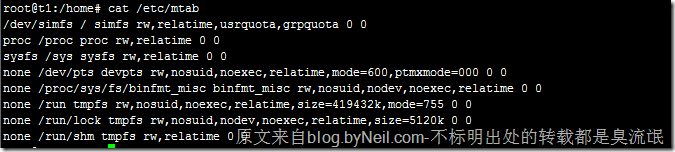
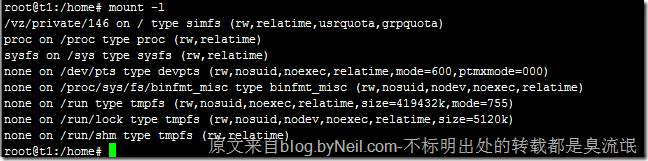
mtab 文件记录的是,当前已挂载的分区信息。每当 mount 挂载分区、umount 卸载分区,都会动态更新 mtab,mtab 总是保持着当前系统中已挂载的分区信息,fdisk、df 这类程序,必须要读取 mtab 文件,才能获得当前系统中的分区挂载情况。 原文来自 blog.byneil.com
root@t1:/home# cat /etc/mtab
/dev/simfs / simfs rw,relatime,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
proc /proc proc rw,relatime 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs rw,relatime 0 0
none /dev/pts devpts rw,nosuid,noexec,relatime,mode=600,ptmxmode=000 0 0
none /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc binfmt_misc rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime 0 0
none /run tmpfs rw,nosuid,noexec,relatime,size=419432k,mode=755 0 0
none /run/lock tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,size=5120k 0 0
none /run/shm tmpfs rw,relatime 0 0df 可以查看当前系统的已挂在的磁盘信息:
fdisk –l 查看系统所有已分区和未分区的磁盘, 并能划分磁盘分区。
mount –l 也能查看当前系统的挂载情况
原文来自 blog.byneil.com
-
联通宽带又在调皮了。给我分配内网ip
-
rsync 远程同步文件
rsync 有两种工作方式, 这里用的是“方式”这个词,而不是“模式”。注意区分。
第一种方式是 服务器--客户端方式。
在这种方式下, 服务端启动daemon 守护进程, 监听在端口 873, 并配置需要同步的模块。 然后客户端直接链接到873端口,通过认证,并同步。
其中,同步用的账号和密码都是rsync专用的,在rsync配置文件中独立配置。 于系统账号无关。
服务端运行rsync进程在daemon模式下, 客户端是普通的rsync进程。
这种模式下,客户端只能同步服务端事先配置的模块(目录)。 不能访问其他路径。
服务端配置方法参考:
第二种方式, 通过ssh链接。
这种方式下, 无需事先配置远程服务端。
本机 rsync 进程 直接通过 ssh 通道连接到远程, 并在远程ssh通道执行命令: rsync –******
本地rsync进程和远程rsync进程 通过自己的标准输入和标准输出 互相通信。 具体的说就是,本地进程监听ssh通道的远程回显当做输入, 把自己的的输出通过ssh通道发送给远程。 而远程的rsync进程就一样, 也会监听ssh通道的输入,当做自己的输入,然后把自己的输出写入到ssh通道。
于是, 远程rsync进程和本地rsync进程就通过这种方式同步文件。
这种情况,无需事先配置远程服务端, 只要你有ssh权限登录,就能同步。
同步的路径无限制。 当然只能访问你的ssh账号所能访问的目录。 如果你是root那就是无限制了。
这两种工作方式下,只是传输的通道不一样,第一种是直接走socket通道。 第二种是走的ssh通道。
安全性显而易见。
两种方式下,rsync都使用自有协议进行同步,所以可以携带的参数都是没有区别的。
具体实例:
rsync 的一般形式:
2: rsync -options SRC DEST当通过ssh链接时, 有时需要指定ssh端口, 请使用这个方式:
1: rsync -options -e "ssh -p 10000" SRC DEST
(注意,是否使用ssh通道,与上面这个参数没有必然联系。我这里指定了10000端口)
我们以从远程 向 本地拷贝为例,
这个时候, SRC 应该是远程地址.
其形式应该是:
如果远程是daemon模式:
MODE是远程daemon事先配置好的 模块名字。这里只能使用已经配好的模块名字,不能使用路径。
注意HOST于MODE之间有两个冒号。 这是rsync用于区分模式的唯一方法。
例子,拷贝远程模块到本地:
1: rsync -vzrtopg --progress --delete user1@192.168.168.52::WEB /tmp/把远程的 WEB模块,拷贝到本地的tmp目录。
或者是:
直接使用ssh模式:
1: USER@HOST:Folder这里,后面跟的直接是Folder的完整路径。 当然是USER所能访问的地方。
注意这里HOST和Folder之间用的是一个冒号, rsync由此判断使用ssh通道。而不是直接连接远端的873端口。
例子:
1: rsync -vzrtopg --progress --delete root@192.168.168.52:/home/wwwroot/ /tmp/这里是使用root用户登录远程服务器, 并把远程的 /home/wwwroot/ 目录同步到本地的 tmp 目录。注意与前一种的区别, 只有一个冒号。 这里会提示输入远程root的密码,如果已经配置了public key ssh 登录远程机器,就无需输入密码了。
常用rsync命令参数:
1: rsync -vzacu /home/wwwroot root@198.***.***.***:/home/ --exclude "wwwroot/index" -e "ssh -p 22"
这是一个通过ssh通道从本地推送到远程的例子。 把本地的/home/wwwroot 推送到远程的/home下面。
参数说明,
-z 表示传输过程压缩
-a 表示采用归档模式, 拷贝文件时,保留文件的属主,用户组,权限等等信息。
-c 表示校验文件checksum
-u 表示update,只传送更新的文件。rsync会比较文件的修改时间。只有较新的文件才会被同步。
参考:
Rsync命令参数详解 - 技术文档 - 系统管理 Linux时代 - 开源、自由、共享 - 中国最大的Linux技术社区